Exchange 2010/2007 to 2013 Migration and Co-existence Guide
We don’t have a lot of guides out there helping with a step by step guide for the migration and co-existence of Exchange 2010/2007 to Exchange 2013So, here you go !!!
Update:
If you are planning to employ a third party product for migration – look no further. CodeTwo is a mature and reliable product for full blown Exchange migraiton from
Exchange 2003/2007/2010 – cross forest or cross domain migration:
Take a look here:
CodeTwo Exchange migration for Exchange 2003 to 2010/2013: Operational review: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/11/24/codetwo-exchange-migration/
Download here:
Download Codetwo for free: http://www.codetwo.com/exchange-migration/
Before you proceed with the actual migration steps, these articles may be of interest to you:
Exchange 2013 CAS Role Demystified: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/05/22/exchange-2013-cas/
Exchange 2013 High Availability demystified: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/05/23/e2013-ha-demystified/
Load Balancing Exchange Server 2013 – Good to know stuff: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/06/05/load-balancing/
Public Folders Migration from Exchange 2007/2010 to Exchange 2013: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/04/18/exchange2013-public-folders/
Upgrade from Exchange 2013 CU1 or RTM to CU2: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/07/10/install-e2013-cu2/
Monitoring and troubleshooting Exchange using powershell: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/07/23/monitoring-powershell/
For Complex Exchange 2007 migration check the common errors here – http://blogs.technet.com/b/exchange/archive/2007/09/10/3403885.aspx
Check our multisite url and authentication blog here – https://msexchangeguru.com/2015/08/22/e20132007-urlsauth-multiadsite/
Preparing Exchange 2010/2007
-
Install the hotfix 2550886 for DAG failover improvements on Exchange 2010/2007 DAG servers.
-
Login to the Exchange 2010/2007 server with Schema Admins, enterprise admins, domain admins and organization management group member id as SP 3 will extend the schema.
-
Install Exchange 2010/2007 SP3 on all the exchange 2010/2007 servers in CAS then HT then mailbox role order if they are not on the same server
SP3 can be downloaded from the below link:
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=36768
-
Check the below link for SP3 installation steps
https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/04/03/exchange-2010/2007-sp3/
Installing Exchange 2013
-
I would suggest going for Windows 2012 for Exchange 2013 but you can use windows 2008 R2 SP1 as well.
-
Install the windows 2012 server or Windows 2008 R2 SP1 on a new server and join the domain. It can be virtual or physical. Now Microsoft support virtualized mailbox role.
-
Run the windows update and install all the recommended updates.
-
You might like to configure windows NLB if you don’t have NLB hardware. Check the below blog on it. (optional) https://msexchangeguru.com/
2013/08/14/windowsnlb/ - For Active Directory preparation check the “step 3 preparing active directory” at the blog mentioned below: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/04/29/install-e2013/
- Install the following prerequisites for Exchange 2013
For Windows 2012:
-
Open Windows PowerShell.
-
Run the following command to install the required Windows components.
Install-WindowsFeature AS-HTTP-Activation, Desktop-Experience, NET-Framework-45-Features, RPC-over-HTTP-proxy, RSAT-Clustering, RSAT-Clustering-CmdInterface, RSAT-Clustering-Mgmt, RSAT-Clustering-PowerShell, Web-Mgmt-Console, WAS-Process-Model, Web-Asp-Net45, Web-Basic-Auth, Web-Client-Auth, Web-Digest-Auth, Web-Dir-Browsing, Web-Dyn-Compression, Web-Http-Errors, Web-Http-Logging, Web-Http-Redirect, Web-Http-Tracing, Web-ISAPI-Ext, Web-ISAPI-Filter, Web-Lgcy-Mgmt-Console, Web-Metabase, Web-Mgmt-Console, Web-Mgmt-Service, Web-Net-Ext45, Web-Request-Monitor, Web-Server, Web-Stat-Compression, Web-Static-Content, Web-Windows-Auth, Web-WMI, Windows-Identity-Foundation
-
Restart the server.
-
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=34992
-
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=17062
-
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=26604
For Windows 2008:
-
Open Windows PowerShell.
-
Run the following command to load the Server Manager module.
Import-Module ServerManager
-
Run the following command to install the required Windows components.
Add-WindowsFeature Desktop-Experience, NET-Framework, NET-HTTP-Activation, RPC-over-HTTP-proxy, RSAT-Clustering, RSAT-Web-Server, WAS-Process-Model, Web-Asp-Net, Web-Basic-Auth, Web-Client-Auth, Web-Digest-Auth, Web-Dir-Browsing, Web-Dyn-Compression, Web-Http-Errors, Web-Http-Logging, Web-Http-Redirect, Web-Http-Tracing, Web-ISAPI-Ext, Web-ISAPI-Filter, Web-Lgcy-Mgmt-Console, Web-Metabase, Web-Mgmt-Console, Web-Mgmt-Service, Web-Net-Ext, Web-Request-Monitor, Web-Server, Web-Stat-Compression, Web-Static-Content, Web-Windows-Auth, Web-WMI
-
Restart the server
-
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/5a4x27ek(VS.110).aspx
-
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=34595
-
Microsoft Unified Communications Managed API 4.0, Core Runtime 64-bit
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=34992
-
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=17062
-
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=26604
6. Restart the server
7. Exchange 2013 Installation – Please follow the below link for the Exchange 2013 installation: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/04/29/install-e2013/or Exchange 2013 SP1installation: https://msexchangeguru.com/2014/03/02/e2013sp1-installationupgrade/
Imp: You can directly install Exchange 2013 CU1 as well. If you directly install CU1 then you can skip step 12 – Testing mailbox move without CU1. If you are installing CU2 make sure you are installing CU2 V2.
If you are doing new installation then you can directly install Exchange 2013 CU1 which itself is a full setup. You can follow same schema update and AD preparation steps.
After Exchange 2013 installation the biggest challenge will be how to login to the EAC, there is no mailbox on Exchange 2013 and redirection or proxy is not configured to use the existing Exchange admin user.
If you are trying to access EAC for the first time and your mailbox is on Exchange 2010, you need to use the URL in the format:
https://Exchange2013ServerName/ecp?ExchClientVer=15
This is because in a co-existence scenario, your mailbox is still housed on the Exchange 2010 mailbox server, the browser will default to the Exchange Server 2010 ECP. Now if you want to access the Exchange 2010 ECP and your mailbox resides on an Exchange 2013 mailbox server, use the following URL:
https://Exchange2010ServerName/ecp?ExchClientVer=14.
Take a look at:
Working with EAC or Exchange administration center in Exchange 2013 – Part1: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/01/16/eac-exchange-2013/
So you need to create a mailbox to administer Exchange 2013. We will follow the below steps:
- Create a mailbox in Exchange 2013 mailbox database.
- “New-Mailbox –name 2013Admin –userPrincipalName 2013Admin@domain.com –Database “2013 DBName””
-
Run Get-mailboxdatabase to check the database name
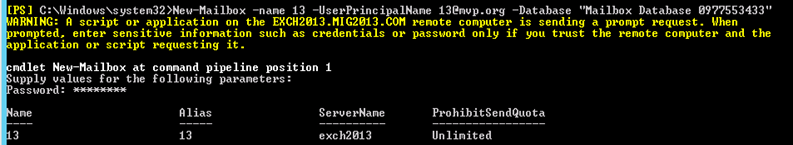
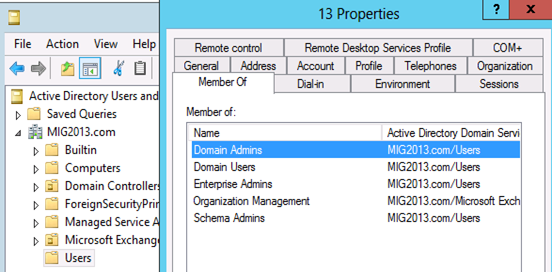
4. Give the permission to the mailbox to Administrate EAC.
Add the following group membership:
Domain Admins
Schema Admins
Enterprise Admins
Organization Management
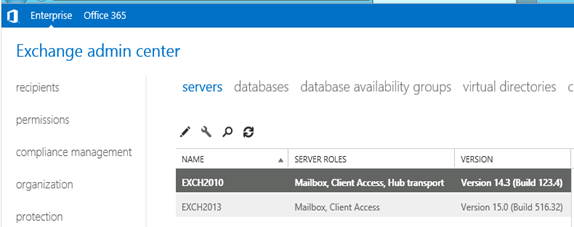
Test mailbox migration without CU1 for Exchange 2013
-
Now, you should be able to login to EAC by going to the url https://localhost/ECP. If you will test the mailbox migration from Exchange 2010/2007 to Exchange 2013 before CU1 for Exchange 2013, it will be working but full co-existence will not work so it is a necessity to install CU1. As an example my Servers are mentioned below:
- EAC will show Databases from both the servers
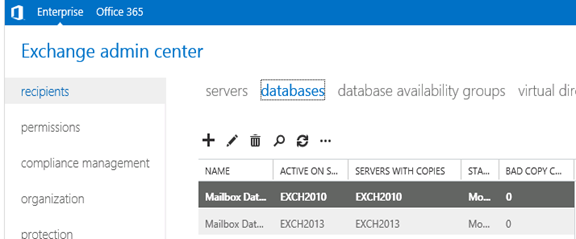
- Now I am migrating the mailbox being Exchange 2010/2007 on SP3 and Exchange 2013 without CU1.
Created new mailbox in Exchange 2010/2007, you can see 2013 database is not showing here
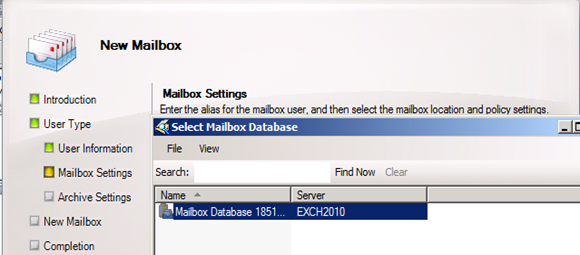
- Database before move
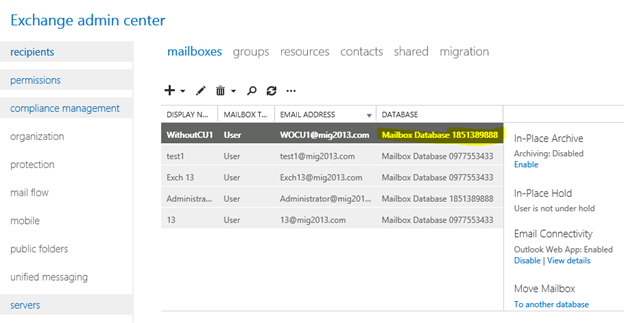
- I have moved the mailbox from Exchange 2013 EAC to Exchange 2013 database. Now click on migration to check the status
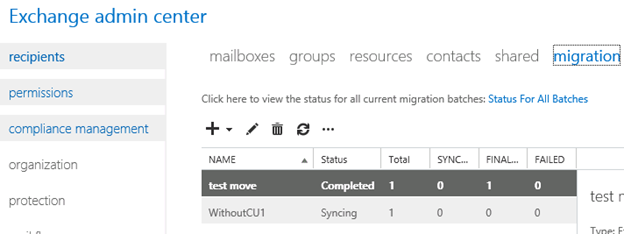
- Now Refresh and you will see completed depends on the size of mailbox.
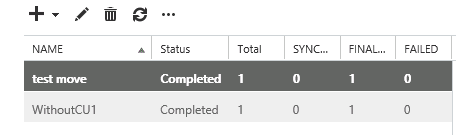
- Check the Database name has changed
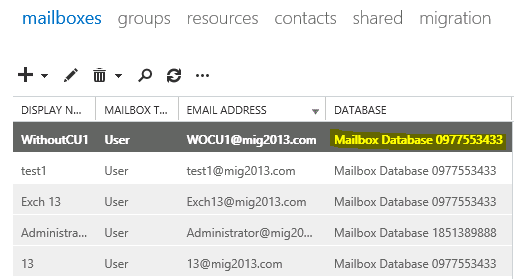
Continue the Exchange 2013 CU1 installation
5. If you have not install CU1 version of exchange 2013 then this is the time to install Exchange 2013 Cumulative update 1 so that we avoid any co-existence issue. If you are doing new installation then you can directly install Exchange 2013 CU1 which itself is a full setup. You can follow same schema update and AD preparation steps mentioned in the Exchange 2013 installation article
Update 4/7/2014: Now – We can go for SP1 – https://msexchangeguru.com/2014/03/02/e2013sp1-installationupgrade/
6. Download the Exchange 2013 from the below link which is an Exchange 2013 setup with Cumulative update
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=38176
7. Install the Exchange 2013 CU 1 with the help of below link:
https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/04/15/e2013-cu1-2/
Configuring Exchange 2013 and network
-
Transport Configuration
-
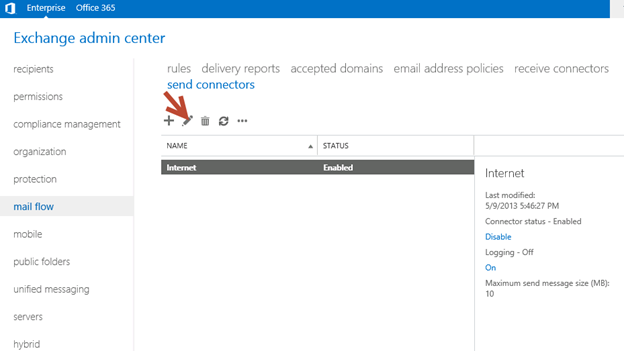
Send connector
1. Exchange 2013 reads exchange 2010/2007 send connector information. Click on the pencil icon to check and add exchange 2013 in the same send connector.
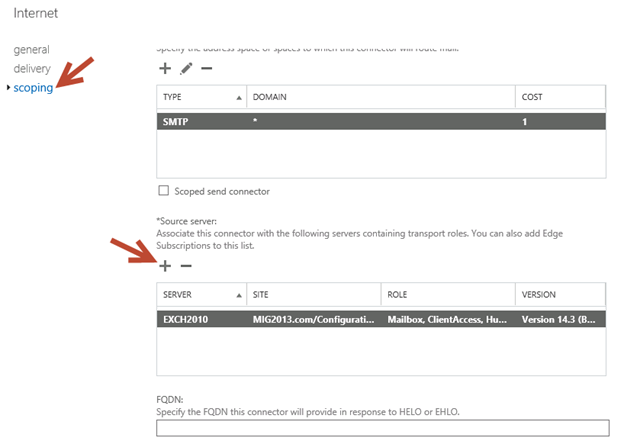
2. Click on scoping and + icon to add the server
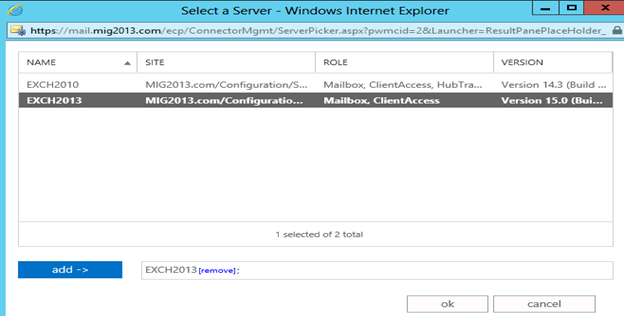
3. Select the server and add, then click on and save. Send connector configuration completed.
3. Receive Connector
1. Add a receive connector as per the current connector configuration.
2. Select the 2013 server, oh what we have 5 connectors for what. Let me explain here.
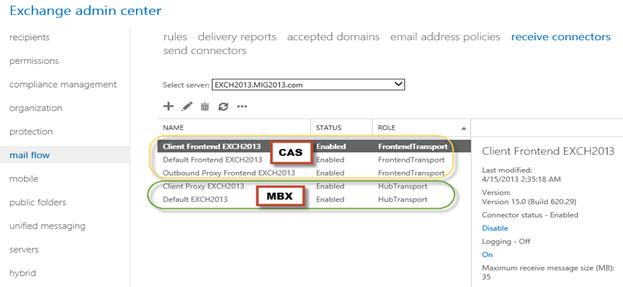
3. You can see all 5 together here as I have CAS and Mailbox on same server. First 3 are for the CAS connector and remain 2 are for mailbox role.
4. I would link to explain the transport pipe line here which consists of the following services:
Front End Transport service – This service runs on all Client Access servers and acts as a stateless proxy for all inbound and outbound external SMTP traffic for the Exchange 2013 organization. The Front End Transport service doesn’t inspect message content, only communicates with the Transport service on a Mailbox server, and doesn’t queue any messages locally.
Transport service – This service runs on all Mailbox servers and is virtually identical to the Hub Transport server role in previous versions of Exchange. The Transport service handles all SMTP mail flow for the organization, performs message categorization, and performs message content inspection. Unlike previous versions of Exchange, the Transport service never communicates directly with mailbox databases. That task is now handled by the Mailbox Transport service. The Transport service routes messages between the Mailbox Transport service, the Transport service, and the Front End Transport service.
Mailbox Transport service – This service runs on all Mailbox servers and consists of two separate services: the Mailbox Transport Submission service and Mailbox Transport Delivery service. The Mailbox Transport Delivery service receives SMTP messages from the Transport service on the local Mailbox server or on other Mailbox servers, and connects to the local mailbox database using an Exchange remote procedure call (RPC) to deliver the message. The Mailbox Transport Submission service connects to the local mailbox database using RPC to retrieve messages, and submits the messages over SMTP to the Transport service on the local Mailbox server, or on other Mailbox servers. The Mailbox Transport Submission service has access to the same routing topology information as the Transport service. Like the Front End Transport service, the Mailbox Transport service also doesn’t queue any messages locally.
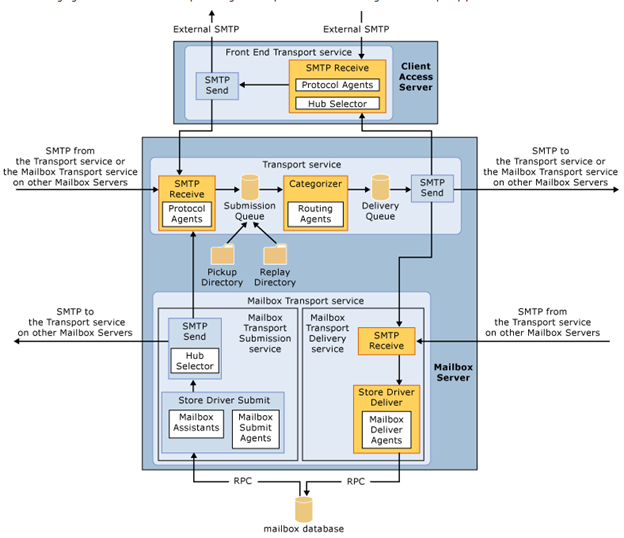 (from TechNet)
(from TechNet)
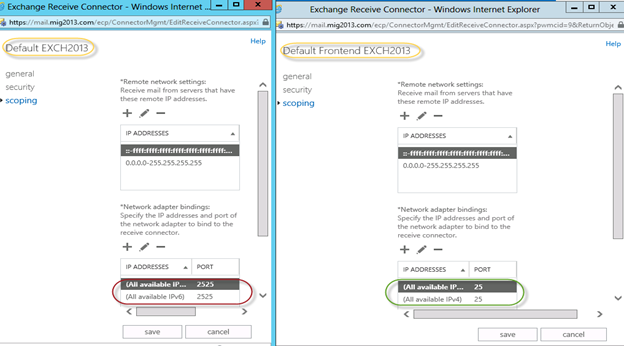
5. Here are the details about the receive connectors
When you install a Mailbox server running the Transport service, two Receive connectors are created. No additional Receive connectors are needed for typical operation, and in most cases the default Receive connectors don’t require a configuration change. These connectors are the following:
Default <server name> Accepts connections from Mailbox servers running the Transport service and from Edge servers.
Client Proxy <server name> Accepts connections from front-end servers. Typically, messages are sent to a front-end server over SMTP.
During installation, three Receive connectors are created on the Front End transport, or Client Access server. The default Front End Receive connector is configured to accept SMTP communications from all IP address ranges. Additionally, there is a Receive connector that can act as an outbound proxy for messages sent to the front-end server from Mailbox servers. Finally, there is a secure Receive connector configured to accept messages encrypted with Transport Layer Security (TLS). These connectors are the following:
Default FrontEnd <server name> Accepts connections from SMTP senders over port 25. This is the common messaging entry point into your organization.
Outbound Proxy Frontend <server name> Accepts messages from a Send Connector on a back-end server, with front-end proxy enabled.
By default we don’t route the outgoing email to CAS. If we have some mailgaurd or compliance requirement on a separate CAS server then we can use it. If we have CAS and mailbox role on the same server then we don’t need to configure this connector. We can simply disable it.
Client Frontend <server name> Accepts secure connections, with Transport Layer Security (TLS) applied.
6. So we have to configure “Default Frontend Servername” connector which is accepting the emails on port 25. Yes this is very important when you have both role on one server then Frontend will be 25 and backend will be 2525
7. You might need to check email address policies, this might needs to re-apply. If we have more than 3000 mailboxes then it is suggest applying from EMS.
To understand the mailflow we can read the below article: https://msexchangeguru.com/2012/08/09/e2013-mailflow/
Exchange 2013 Certificates
Create a new Exchange certificate on Exchange 2013: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/01/18/e2013-certificate/
Use current certificate
For Export and import of the cert Please check here – https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/06/29/import-cert-e2013/
- Export the cert from Exchange 2010
- Import the cert to Exchange 2013
- Configure the external url. This is very simple in exchange 2013. You don’t need to go to every virtual directory property.
- Select the wrench mentioned below windows
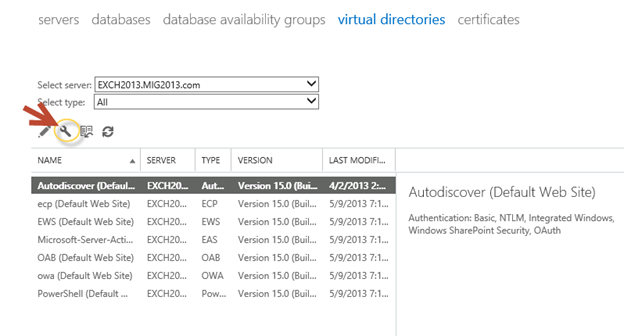
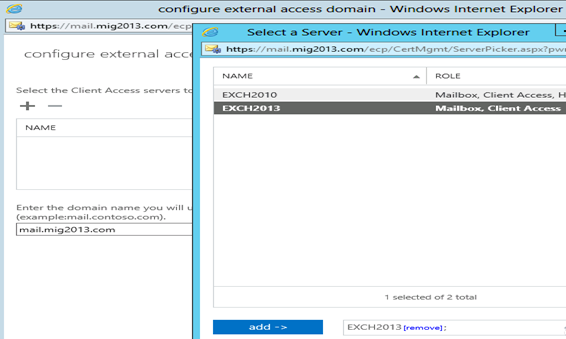
5. Then this wizard will open, select the exchange 2013 server and give the external url and save it.
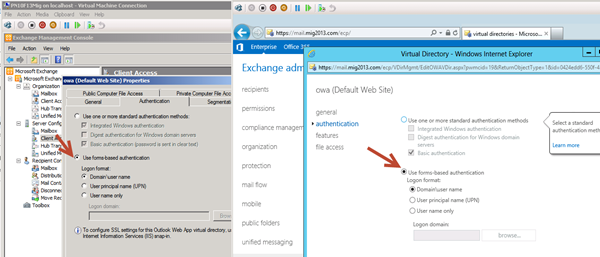
6. CAS Authentication will be “Use form-based authentication” on both Exchange 2013 and Exchange 2010/2007.
Database availability Group
We would like to configure a DAG for high availability with multiple databases. So we have 2 options.
1. DAG with IP. Check the below link to create a DAG with IP
https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/01/17/e2013-dag/
2. DAG without IP – This needs Exchange 2013 SP1 on Windows 2012 R2
Check the below link to create IP less DAG
https://msexchangeguru.com/2014/03/21/e2013sp1-ip-less-dag/
Update Feb 2015: If you have 2 datacenters expanded DAG then now you can configure your FSW in Azure which means your DAG can be configurable to 3 Data center expanded automated DAG. This will allow you to completely shut down the data center without loosing production connectivity. Here is the link to configure FSW in Azure – Using a Microsoft Azure VM as a DAG witness server
Move Arbitration and Discovery Search mailboxes
Follow the below steps to move all arbitration and discovery search mailboxes to final 2013 database.
Open EMS with run as administrator and run the following cmds
Get‐Mailbox –Arbitration | New‐MoveRequest –TargetDatabase TargetDBName
Get-Mailbox “*Discovery*” | New‐MoveRequest –TargetDatabase TargetDBName
Unified Messaging: Upgrade Exchange 2010 UM to Exchange 2013 UM
This is the optional step only for unified messaging configured organizations.
Please follow the below link to upgrade exchange 2010 UM to Exchange 2013 UM
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn169226(v=exchg.150).aspx
Configure Enabled Outlook Anywhere
For Exchange 2007
Set-OutlookAnywhere -Identity “2010 CasServerNameRpc (Default Web Site)” -ClientAuthenticationMethod Basic -SSLOffloading $False -ExternalHostName mail.domain.com -IISAuthenticationMethods {NTLM,Basic}
For Exchange 2010
Set-OutlookAnywhere -Identity “2010 CasServerNameRpc (Default Web Site)” -ClientAuthenticationMethod Basic -SSLOffloading $False -ExternalHostName mail.domain.com -IISAuthenticationMethods NTLM, Basic
Configure OAB
Run the below command to configure OAB for all databases
Get-MailboxDatabase | Set-MailboxDatabase -OfflineAddressBook “Default Offline Address List (Ex2013)”
Default Offline Address List (Ex2013) can be replaced by your custom named OAB.
Enabling and Configuring Outlook Anywhere
For Exchange 2007
Get-ExchangeServer | Where {($_.AdminDisplayVersion -Like “Version 8*”) -And ($_.ServerRole -Like “*ClientAccess*”)} | Get-ClientAccessServer | Where {$_.OutlookAnywhereEnabled -Eq $False} | Enable-OutlookAnywhere -ClientAuthenticationMethod Basic -SSLOffloading $False -ExternalHostName mail.domain.com -IISAuthenticationMethods NTLM, Basic
For Exchange 2010
Get-ExchangeServer | Where {($_.AdminDisplayVersion -Like “Version 14*”) -And ($_.ServerRole -Like “*ClientAccess*”)} | Get-ClientAccessServer | Where {$_.OutlookAnywhereEnabled -Eq $False} | Enable-OutlookAnywhere -ClientAuthenticationMethod Basic -SSLOffloading $False -ExternalHostName mail.domain.com -IISAuthenticationMethods NTLM, Basic
SCP – Service Connection Point Configuration:
Run the below command to configure SCP on Exchange Management Shell of 2007/2010/2013 separately:
get-ClientAccessServer | Set-ClientAccessServer -AutoDiscoverServiceInternalUri https://autodiscover.domainname/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml
SCP might be already configured on 2007/2010 server so you can also check it and use the same -AutoDiscoverServiceInternalUri. Run the below cmd to get current SCP on 2013 Shell
get-ClientAccessServer | fl name,AutoDiscoverServiceInternalUri
RemoteDomain:
Run the below cmd in EMS to allow auto forwarding, oof, auto reply and disable the possibility of winmail.dat from domino server.
Set-remoteDomain -AutoReplyEnabled $True -AutoForwardEnabled $True -TNEFEnabled $False -AllowedOOFType External
Pop/IMAP:
If you have pop3/imap4 users then you might like to configure 2013 for some addition configuration.
1. Configure the Basic authentication on EAC for CAS 2013
2. Start the services and change them to automatic.
Email address policy:
You might need this step if you organization was initially created on Exchange 2003.
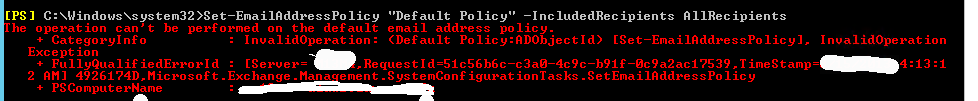
1. Create a new email address policy if there is only one “Default Policy”.
2. Change the attributes of existing email address policy by running the below cmd
Get-emailaddresspolicy | Set-EmailAddressPolicy -RecipientFilter “Alias -ne $null” -IncludedRecipients AllRecipients
3. If you see the below error for the default policy then Remove “Default Policy” which was created in 2003 and will be in ready only mode in Exchange 2013.
Clean up health mailboxes:
When you remove default mailbox database, it does not remove health mailboxes which we can check by running the cmd and below warning will come. Health mailboxes are for the health service and they are specific for every database so we don’t need to move them rather we need to remove them.
Get-mailbox –monitoring
Mailboxes/HealthMailbox94863fe5394447619ec45c4e6b2dd971 has been corrupted, and it’s in an inconsistent state.
The following validation errors happened: WARNING: Database is mandatory on UserMailbox.
To fix this we need to delete user account in dsa.msc at yourdomain/Microsoft Exchange System Objects/Monitoring Mailboxes
Important: At the point configure your outlook for Exchange 2007/2010 mailbox and 2013 mailbox. If both are working from Internet then move to the next step.
CutOver :Updated 2007 part Feb 2015
Now it is the time to do cutover means point the connections to Exchange 2013. It can be done in few simple steps.
1. Create or change Public and Private DNS pointers.
a. autodiscover.domain.com will be pointing to the CAS 2010/2007 or Load balancer of CAS 2010/2007. So change the IP from Exchange 2010/2007 to 2013. In case of new installation or exchange 2007 environment we need to create new host record in DNS. This will be done on both internal and external
b. mail.domain.com (OWA/activesync/RPCoverhttp/mapioverhttp) Change the IP from Exchange 2010/2007 to Exchange 2013 CAS servers or Load balancer.
c. Create Legacy.domain.com host record in case of exchange 2007 co-existence in both public and private DNS. This will point to Exchange 2007 CAS servers or Exchange 2007 l0ad balancer CAS VIP.
2. Point your Spam Guard to forward all the emails to exchange 2013 to receive incoming mail via Exchange 2013.
3. Configure Spam Guard to accept emails from all Exchange 2013 Mailbox servers.
4. Configure all other application to send email to the Exchange 2013 Mailbox Servers.
5. Update PTR and SPF record if Exchange 2013 are sending the emails out directly.
6. In case of Exchange 2007, we need to update the following URLs and Authentications as well.
- EWS – Run the below cmd on Exchange 2007 EMS
Get-WebServicesVirtualDirectory | Set-WebServicesVirtualDirectory -ExternalUrl https://legacy.Domain.com/EWS/Exchange.asmx -internalurl https://legacy.Domain.com/EWS/Exchange.asmx
- OWA – Run the below cmd on Exchange 2007 EMS
Get-OWAVirtualDirectory | Set-OWAVirtualDirectory -ExternalUrl https://legacy.Domain.com/OWA -internalurl https://legacy.Domain.com/OWA
- OWA – Run the below command to change the authentication method in Exchange 2007 EMS
Get-owaVirtualDirectory -identity “CASName1OWA (Default web site)” | Set-OwaVirtualDirectory -ExternalAuthenticationMethods FBA,basic
Exchange 2013 Mailbox Migration
So what are we waiting for… Let us begin the mailbox migration.
- Now you can run the following cmdlet to move bulk or single mailbox
Get-Mailbox –Database “Exchange 2010/2007/2007 Database” –OrganizationUnit “DN of the OU” | New-Move Request –TargetDatabase “Exchange 2013 Database”
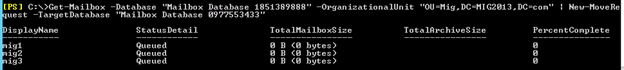
2. You can monitor the migration by running the following cmdlet or going to the migration tab in EAC:
Get-MoveRequest

3. Once completed it will show the below window
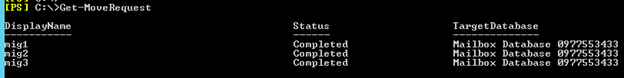
For Cross forest mailbox migration check this link: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/11/02/e2013crossforestmigration/
Public Folder Migration
-
Once we complete all mailbox migration then we can start the Public Folders migration.
For Public Folder migration use the below Link:
https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/04/18/exchange2013-public-folders/
- Test everything working and shutdown Exchange 2010/2007 server for 1 production week and observe if no issue reported then go ahead with the Exchange 2010/2007 removal process.
Known Issues:
Active Sync Config without Domain Name: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/08/06/e2013mobiledomain/
OWA redirection broken page and SSL: http://www.expta.com/2013/05/owa-2013-cu1-redirection-is-broken-for.html – This was fixed in CU3
If you have pop/imap user go for CU2: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/08/04/e2013popimapauth/
Mailflow misconfiguration: https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/08/03/e2013-2010mailflowissue/
Certifacate and cryptographic provider Issue: http://msitpros.com/?p=1770
Legacy Removal
-
Now we are in a position to remove exchange 2010. We can follow the below link for the exchange 2010/2007 removal.
https://msexchangeguru.com/2013/09/01/e20102007decomposte2013mig/
Hit us with questions
Prabhat Nigam | MVP Exchange
Team @MSExchangeGuru
Keywords: Exchange 2010 to exchange 2013 migration, how to migrate to Exchange 2013




June 15th, 2015 at 12:21 pm
IPv6 disabled on both Exchange 2007 and 2013?
June 15th, 2015 at 12:23 pm
I would say in the whole infrastructure including all Exchange and AD unless you have a requirement of IPv6 like direct access.
June 15th, 2015 at 12:23 pm
found that it says to disable if both Ex2k7 mailbox and CAs roles on same box…
June 15th, 2015 at 12:32 pm
IP6 is disabled on all Dc’s and Exchange 2013.
Question Does Exchange have a System file checker like Windows, to make sure all files are there? Can We run Exchange Best Practice Analyzer to check
this exchange server if ok?
June 15th, 2015 at 12:57 pm
I_v6. Hmm. we turned off IPV6 on an Exchange 2010 install and it got screwed up. Microsoft told us to re-enable it. Hmmm. Hoepfully, it will not get screwed up. Will let you know.
June 15th, 2015 at 1:01 pm
you need to disable from registry key disabledcomponents value ffffffff.
June 18th, 2015 at 10:27 am
Dear ALL Exchange guru:
I have a question regarding Exchange schema preparation: Our exchange is currently based in cross forest and planning to bring back Exchange in-house. Our Forest/domain which currently has no Exchange installed but previously had Exchange 2003 and therefore the schema is currently up to Exchange 2003. In order to prepare the environment for Exchange 2013 DO WE NEED to clear this schema or do anything tiding up before apply schema prep.
I am not aware of any compatibility issues on schema upgrade but apparently there is.
thank you all,
June 18th, 2015 at 10:57 am
you can try this. From a forum
In a nutshell, the proper way to get Exchange out of Active Directory is to run “update /removeOrg” from an SP2 installer. Sometimes it doesn’t work. For me, it was spewing errors about trying to prepare the forest (why, when I’m trying to unprepare the forest?). After a day of search, it seemed like I was the only one ever to need to manually extract Exchange from Active Directory. What I ended up doing was quite simple. I ran ADSI, and removed the Microsoft Exchange OU in the default schema. That’s the obvious one. But that wasn’t enough. I also needed to switch to the “Configuration” schema (right click the domain name in ADSI on the left-hand tree and choose “Settings”, and change the “Select a well known naming context” dropdown to “Configuration”), drill down to “Services” and remove the “Microsoft Exchange” CN there as well.
Presto, no more Exchange!
If you want/need to, you should also remove the groups in Active Directory, but this appears to be unnecessary for moving to Exchange 2007.
June 18th, 2015 at 11:50 am
Hi Babalou,
Interesting stuff. but my question is does it require to extract or remove the Exchange Org before preparing the environment for Exchange 2013.
regards
June 18th, 2015 at 12:46 pm
I would assume so. I have had this happen with one of my clients. They had Exchange 2003. The Exchange server crashed. The in house IT guys decided to just install Exchange 2007 and it got messed up. I am sure because it needed to contact the old server.. I ended up doing what I told you. It worked for me…The client IT never bothered to call us until… Ended up moving them to hosted Exchange later on because their IT could not handle Exchange very well.
June 18th, 2015 at 8:35 pm
No need to remove exchange org.
The right way is remove application from ADD and remove programs. Before this follow my blog – https://msexchangeguru.com/2014/05/31/e2003removale2010mixedmode/
=========
Greg
In your case you should have tried to install 2003. Even if one was crash it could have been restored. Removing org is not recommended.
June 19th, 2015 at 3:16 am
Hi there,
Last problem I’m having is Outlook connectivity… I’m having issues with RPC – I was getting this error:
The RPC_S_SERVER_UNAVAILABLE error (0x6ba) was thrown by the RPC Runtime process.
But now seems to be this one:
Testing HTTP Authentication Methods for URL https://mail.domain.com/rpc/rpcproxy.dll?973c4148-4055-4290-923b-48db74ddb4fb@arts.ryerson.ca:6002.
The HTTP authentication test failed.
Additional Details
An HTTP 500 response was returned from Unknown.
HTTP Response Headers:
Content-Length: 3423
Cache-Control: private
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Date: Fri, 19 Jun 2015 07:02:56 GMT
Server: Microsoft-IIS/8.5
X-AspNet-Version: 4.0.30319
X-Powered-By: ASP.NET
Elapsed Time: 427 ms.
June 19th, 2015 at 9:28 am
ok. Could not find the media. Plus, they tried to do a direct install of Exchange 2007 and it made things worse. Thanks for the tip…. Unfortunately, not too many Exchange 2003 out there- although I have seen a lot of SBS 2003 🙂
June 19th, 2015 at 9:31 am
I wanted to try that command line option to remove. Did not have the media. Question. I may have asked before. I made my SAN cert. I am going to replace my existing non AN cert on my Exchange 2007. I am going to also import it into the Exchange 2013 server. On which server to I install? I will have the mailbox server, plus that front end Semi CAS Ex2k13 server. Thanks.
June 19th, 2015 at 12:23 pm
You have to install the cert on CAS
June 19th, 2015 at 1:00 pm
perfect. Thanks for the quick reply.
June 20th, 2015 at 2:35 am
What are the authentications on outlook anywhere for 2013 CAS and 2010?
You don’t need to change anything on the mailbox role.
June 21st, 2015 at 8:49 am
Prabhat,
Update so far Exchange 2013 working fine, we have no issues with 2007
mailflow. Did not touch Any send/receive Connectos yet, question though,I migrated a 2007 mailbox to 2013 called tuser3. I can send mail
from 2007 to this user on 2013. 2013 tuser3 can send/receive email
from the Outside. My Problem is when 2013 tuser3 sends mail to 2007
it sits in the exchange 2013 queue and times out with message
6/20/2015 8:15:21 PM – Remote Server at 2007MAIL.mlco.local (192.168.0.17) returned ‘550 4.4.7 QUEUE.Expired; message expired’
6/20/2015 8:05:21 PM – Remote Server at 2007mail.mlco.local (192.168.0.17) returned ‘451 4.4.0 Primary target IP address responded with: “451 5.7.3 Cannot achieve Exchange Server authentication.” Attempted failover to alternate host, but that did not succeed. Either there are no alternate hosts, or delivery failed to all alternate hosts. The last endpoint attempted was 192.168.0.17:25’
Do you have any Idea?
Thanks
June 21st, 2015 at 3:09 pm
Check the receive connector on 2007 if exchange server authentication is checked.
June 21st, 2015 at 8:32 pm
Its not checked should it be?
June 21st, 2015 at 8:39 pm
I got it you were right, I had to check exchange server authentication.
Exchange 2013 can now send to 2007.
I will keep you updated on the migration, again thats for all your help.
June 23rd, 2015 at 1:21 pm
I just finished adding a backend 2013 mailbox server and a front end 2013 CAS server. I moved the administrator mailbox to the Exchange 2013 mailbox server. I can send and receive mail from internal and external to that mailbox. I have not added NAT to the IP of the 2013 front end server yet.
I am trying to configure the receive connectors on the front end CAS 2013 server. I can change the FQDN of the server from the internal NetBIOS name to the FQDN of mail.company.com for the client front end connector. However, when I try to change the Default Front end connector server name from the NetBIOS name to the FQQN, it will not let me. Probably not a big deal since I do not allow inbound SMTP directly to that server. I have an antispam server at my datacenter that forwards through the site to site VPN. If I had no front end spam server, how would I be able to change the name for the Default Frontend connector server name so when people try to telnet to it on port 25, it will not reply with the NetBIOS name? Thanks.
June 24th, 2015 at 2:02 pm
Server FQDN is fine on the receive connector.
June 24th, 2015 at 2:11 pm
It won’t let me change it. It says it has to be the NetBIOS name. I would rather not have external people see what my internal server name is. :/ The client one is set for Internet FQDN. The Default is not and cannot.
June 24th, 2015 at 2:20 pm
Go with default. no issues with netbios name as well.
July 9th, 2015 at 5:45 am
Hi Prabhat,
This is a great article nice work.
I have installed 2 server(1 AD + 1Exchange2013) in my existing SBS2011 with Exchange 2010 Environment. Having 2 problems,
1. When configuring outlook i have to type old exchange server name then it resolves to new server name, if i type new server name it does not configure outlook.
2. i have moved 2 mailboxes to new server email flow is working fine. but when i go to global address book it says connection ot Microsoft exchange unavailable.
Any help would be apprecaited.
July 9th, 2015 at 12:48 pm
For the issue one, your autodiscoverserviceuri should be working to configure the outlook because it will use mailbox guid in place of server-name.
Second issue looks like you DNS is not resolving correctly. Check your DNS. If DNS is fine then run the following command from Exchange 2013 EMS
Get-globaladdresslist | update-globaladdresslist
July 12th, 2015 at 7:47 am
Thanks Prabhat,
Still have same issues, tried almost everything.
Have checked Autodiscoverserivceuri and its working fine,
For DNS checked seems ok to me. not sure where i am doing wrong.
Might be self assigned certificate ?
Thanks.
July 12th, 2015 at 2:06 pm
Did you install 3rd party cert and assigned the iis service?
July 14th, 2015 at 8:09 pm
Yes Thanks Prabhat, did install 3rd Party Cert and it solved my 2nd problem with Global Address List. But still having 1st problem with my Auto discover.
July 14th, 2015 at 8:30 pm
Is the issue with one user or all user?
If it is with one user then Check users AD property like country, city.
July 15th, 2015 at 8:19 am
yes its happening with all users. for explanation, if i setup email for computer joined in domain e.g. USER1 , the autodiscover automatically resolves server to some hexa numbers (ef3457aedf@mydomain.com.au) and email works fine. But if i setup email from any computer not joined in domain, but in same network then i have to put old server name that resolves to new server name. I hope i explained it clearly.
July 15th, 2015 at 4:54 pm
ping autodiscover.emaildomain.com from non-domain joined machine and tell me if you can ping exchange 2013 Cas server or vip.
July 15th, 2015 at 7:37 pm
Thanks Prabhat, Please see result below from ping.
Domain Computer
Ping svmail01- Respond from local ip 192.168.0.12
Ping svmail01.maildomain.local – 192.168.0.12
Ping remote.maildomain.com – Repond from Public IP – I am using remote.maildomain.com.au for my Autodiscover,OWA,OAB
NON Domain Computer:
Ping svmail01 – respond from local IPv6
Ping svmail01 – 192.168.0.12
Ping remote.maildomain.com – resolved to Public IP but does not respond (request time out).
July 15th, 2015 at 9:56 pm
What is remote?
I have asked autodiscover.emaildomain.com
Looks like you have not followed my blog if you have remote.emaildomain.com in autodiscoverserviceinternaluri.
July 16th, 2015 at 7:04 am
instead of Autodiscover.mydomain.com i used remote.mydomain.com , would that be a problem if i use different name than autodiscover
July 16th, 2015 at 3:04 pm
Yes it is an issue. fix it and you will be good.
July 21st, 2015 at 7:00 am
Hi Prabhat,
it’s a wonderful site and great instructions for running Exchange 2013 in co-existence with Exchange 2010. I managed to get Exchange 2013 installed and set up correctly and everything is working fine. I’ve got only 1 very minor issue that I need some advise to look into right direction.
When I move the mailbox from Exchange 2010 to Exchange 2013, once the move is completed – if mailbox is opened in Outlook 2007, users get notification – “The exchange administrator has made the changes and requires you to quit and restart the outlook”. When you click ok, it’s trying to configure the profile and open the outlook – but gives another messsage – “Cannot open your default e-mail folder. Microsoft Exchange is not available. Either there are network problems or the Exchange computer is down for maintenance”. When we click Ok on message – it quits the outlook. However, I can go and setup the outlook profile manually for the mailbox which is migrated to Exchange 2013 and it works fine.
What could be the root cause of this problem? and how can I fix it?
Await your response.
Kind regards,
Vishal.
July 22nd, 2015 at 5:50 am
I did change my autodiscover to autodiscover.mydomain.com , added autodiscover.mydomain.com to 3rd party certificate, still have issue, when i try to config outlook it discovers username and email, when i click NEXT it give green tick to establish network connection, green tick to server setting. But when it goes to third step LOG ON TO SERVER, it give error of connection to MS Exchange not available, then give me option to enter server name, i have to type old server name then it resolves to new server.
if i run this command :get-ClientAccessServer | fl name,AutoDiscoverServiceInternalUri
i get this result for both servers: https://autodiscover.mydomain.com.au/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml
July 24th, 2015 at 8:46 am
Prabhat,
This Sunday we plan on changing the Exchange 2007 connectors to Point to Legacy.***.com and Point The Exchange 2013 Connectors to mail.***.com.
Have a Question about Outlook clients, we have users with Outlook 2007, 2010, and 2013. They are not configured to use Outlook anywhere yet.
When we change the Connectors will this effect them come monday or will they be able to still access their email. Do I need to change all users
to Outlook Anywhere First on each profile before switching connectors???
New Certificates are in place for 2007 and 2013 and working.
Thanks
Russ
July 24th, 2015 at 9:07 am
Did you mean urls for different protocol in place of Connectors?
If yes then make sure to configure legacy for only exchange 2007 owa and ews
Yes, you need to change users to use outlook anywhere before you change DNS pointers to 2013 else 2013 won’t be able to proxy the request for outlook.
July 24th, 2015 at 9:34 am
I am working on a co-existence project for a client. I have Exch 2007 and Exch 2013. When I migrate a mailbox to the 2013 server, mail cannot flow from 2007 to 2013. The 2007 receives the email from outside the organization, but does not deliver it to 2013. I see the email in the queue, and do far no actual fail occurs, the email just sits in the queue. The servers are on the same switch without any firewall in between and all other communications between the servers work. Any help is appreciated. Thanks
July 25th, 2015 at 9:36 am
Solved issue with autodiscover it was becacause of virtual directory not set properly. had to run following command.
Set-AutodiscoverVirtualDirectory -Identity ‘Autodiscover (Default Web Site)’ -InternalUrl ‘https://autodiscover.mydomain.com.au/Autodiscover/Autodiscover.xml’
thanks for you help
July 25th, 2015 at 2:05 pm
You mean in 2010. 2013 does not use and you can’t configure internalurl and externalurl for autodiscovervirtualdirectory
July 26th, 2015 at 5:30 pm
Prabhat,
To Confirm
before we change Connectors and make Exchange 2013 main mail flow, we must make sure all our Clients Outlook profile use Outlook Anywhere instead of mapi etc. Even though their mailbox still resides on Exchange 2007.
We will put our Upgrade on hold for another week, while we go around
and change each users profile.
Thanks Again for you help.
July 26th, 2015 at 6:34 pm
Mail flow does not matter.
it is for the mailbox migration and if you need 2013 to do proxy to 2007 then correct step is to configure outlook anywhere but as far as outlook user use mapi to connect it does not matter. Before migrating exchange 2007 mailbox, you should change the client protocol to outlook anywhere so that they get less popups or no popups.
July 27th, 2015 at 8:59 am
Prabhat,
This morning I went to about 5 users mailbox and for some reason Outlook
Anywhere is configured on their profile. Its set to use Exchange Proxy settings pointing to our mail.XXX.com server. I will continue to check
users profiles today, but what process changed these automatically?? I know I did not change these manually thats for sure.
Thanks
July 27th, 2015 at 1:20 pm
Outlook clients update itself from server but I would doubt it if fast connection is checked.
July 27th, 2015 at 2:20 pm
Both are Unchecked, Should we go around and check use fast connection
on all profiles? Can we do it with a GPO?
July 27th, 2015 at 3:05 pm
You need to check both and gpo can do it.