Disconnected Mailboxes in Exchange2016
A disconnected mailbox is a mailbox entity in the mailbox database that isn’t linked with an Active Directory user account.
We can find two types of disconnected mailboxes in exchange namely Disabled mailboxes and Soft Deleted Mailboxes.
Disabled mailboxes: When an administrator disable or delete the mailbox either using Exchange Administration Center (EAC) or using Exchange Management Shell with Disable-Mailbox or Remove-Mailbox cmdlet, Exchange will holds the deleted mailbox in the mailbox database, and changes the mailbox to a disabled state. The difference between disable and delete is, when you disable a mailbox, it removes the Exchange attributes from the corresponding Active Directory user account, but the user account is retained. When you delete a mailbox, both the Exchange attributes and the Active Directory user account are deleted.
NOTE:
- Disabled and deleted mailboxes are retained in the mailbox database until the deleted mailbox retention period ends, once the retention period ends, the mailbox is permanently deleted or purged. By default 30 days is set as the retention period for the deleted mailbox retention period.
- If a mailbox is deleted using Remove-Mailbox cmdlet and either the Permanent or StoreMailboxIdentity parameter, mailbox will be immediately deleted from the mailbox database.
Command to identify disabled mailboxes in the exchange organization:
Get-MailboxDatabase | Get-MailboxStatistics | Where { $_.DisconnectReason -eq “Disabled” } | ft DisplayName,Database,DisconnectDate

Soft-deleted mailboxes: When an administrator moves a mailbox to a different database, Exchange will not completely delete the mailbox from source database; instead, the will be switched to a soft-deleted state in the source database. Similar to disabled mailboxes, soft-deleted mailboxes are retained in the source database either until the deleted mailbox retention period expires or until the Remove-StoreMailbox cmdlet is used to purge the mailbox.
Command to identify soft-deleted mailboxes in the exchange organization.
Get-MailboxDatabase | Get-MailboxStatistics | Where { $_.DisconnectReason -eq “SoftDeleted” } | ft DisplayName,Database,DisconnectDate

Working with Disabled Mailboxes:
Administrator can perform the below operation before the disabled mailbox gets purged:
- Reconnect it to the same user account.
- Connect it to a different user account which is not mail-enabled,
-
Restore it to a user account that has an existing mailbox.
Example: If a user whose mailbox was deleted and has a new mailbox, administrator can restore the user’s disabled mailbox to the new mailbox.
- Permanently delete the mailbox from the Exchange mailbox database.
Reconnect the disconnected Mailbox:
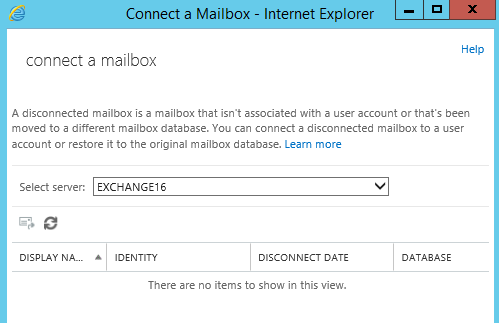
Go to EACàRecepientsàclick on more options (…) as belowà Select Connect a mailbox:
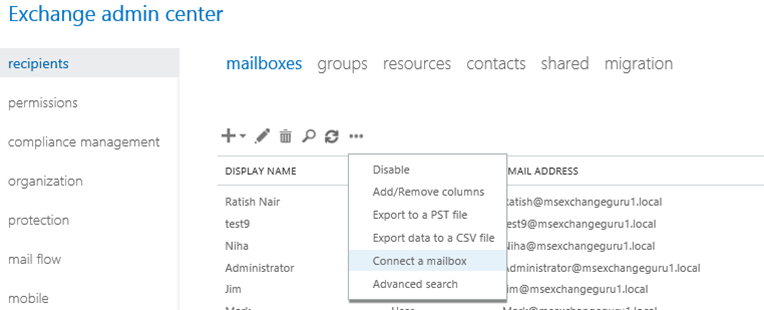
Once we click on Connect a mailbox, it will open new window, select a server if you have more and it will list all disconnected mailboxes under that server:
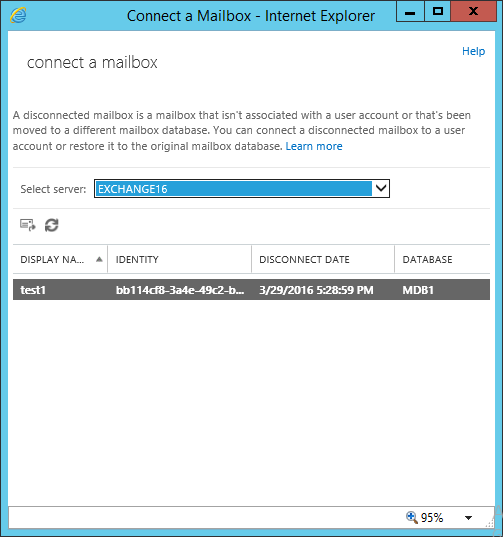
Select the mailbox which you want to connect and clock on connect icon as below:
as below:
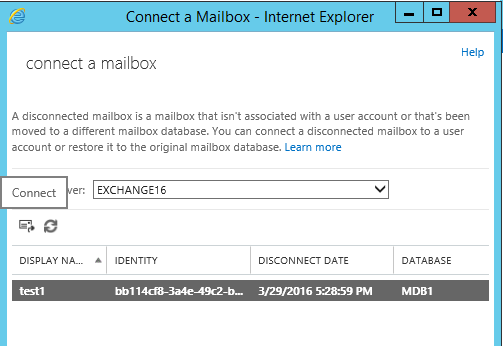
Once connect is clicked, it will provide 2 options:
Either connects to the same user account or Administrator can connect to different user account:
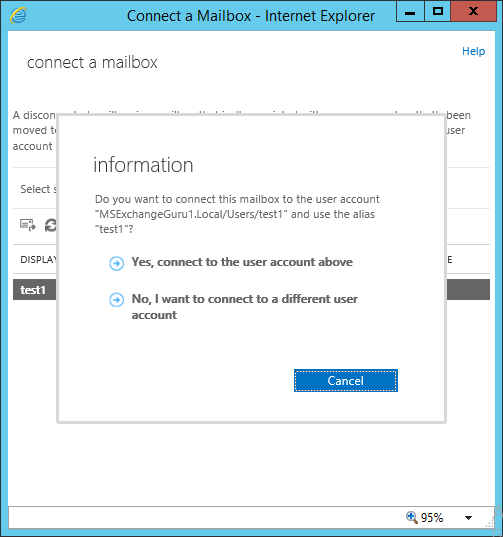
Connect to the same User account:
Connect to Different user account:
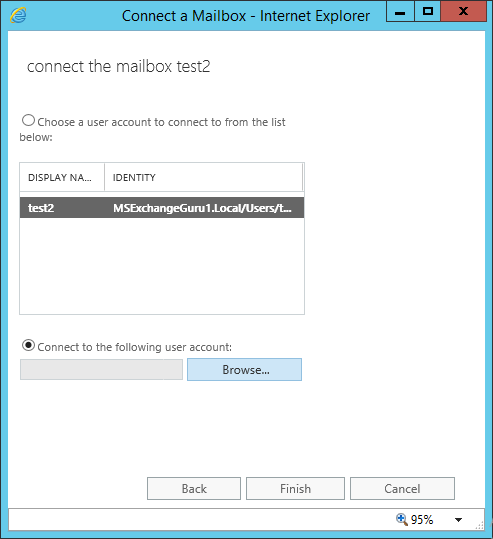
This will provide different options to select the type of the mailbox to be connected as below:

Once we select the mailbox type, new window will open to select the user account, select the user account and click on Finish to connect the mailbox.
Restore the disconnected Mailbox:
When a Deleted mailbox is restored, contents of the mailbox will be copied to the target mailbox. Once the mailbox restore request is completed successfully, it will be retained for 30 days in the database by default, or until it is permanently deleted by an administrator using Remove-StoreMailbox cmdlet.
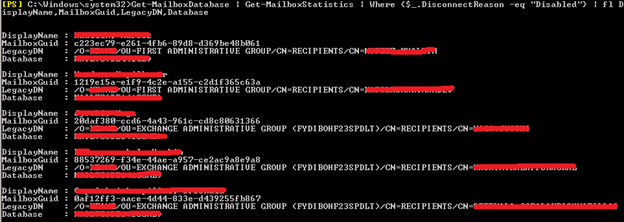
In order to create a mailbox restore request, it’s required to use the display name, legacy distinguished name (DN), or mailbox GUID of the deleted mailbox. Get-MailboxStatistics cmdlet provides the values of the DisplayName, MailboxGuid, and LegacyDN properties for the deleted mailbox which is required to restore.
Get-MailboxDatabase | Get-MailboxStatistics | Where {$_.DisconnectReason -eq “Disabled”} | fl DisplayName,MailboxGuid,LegacyDN,Database
Command to restore the deleted mailbox, which is identified by the SourceStoreMailbox parameter: The AllowLegacyDNMismatch parameter is used so the source mailbox can be restored to a different mailbox, which doesn’t have the same legacy DN value.
New-MailboxRestoreRequest -SourceStoreMailbox <MailboxGUID> -SourceDatabase <database name> -TargetMailbox “<Username>” -AllowLegacyDNMismatch
Command to restore user’s deleted archive mailbox to their current archive mailbox. The AllowLegacyDNMismatch parameter isn’t necessary because a primary mailbox and its equivalent archive mailbox have the same legacy DN.
New-MailboxRestoreRequest -SourceStoreMailbox “<User archive mailbox name> ” -SourceDatabase “Database name” -TargetMailbox <target user email id> -TargetIsArchive
NOTE: Restore of a Deleted mailbox cannot be done using EAC.
Working with disabled archive mailboxes:
If a mailbox is associated with an Archive mailbox, the Archive mailbox is become disconnected when they’re disabled. Similar to a disabled primary mailbox, a disconnected archive mailbox can be connected by using the Connect-Mailbox cmdlet with the Archive parameter.
The primary mailbox and the archive mailbox share the same legacy distinguished name (DN), administrator must connect the archive mailbox to the same user mailbox that it was connected previously. It is not possible to connect the archive mailbox to a different user mailbox.
NOTE:
- If an archive mailbox for a user mailbox is disabled and a new a new archive mailbox is enabled for that same user, that user mailbox will get a new archive mailbox.
- Use Connect-Mailbox cmdlet to connect a primary mailbox to a user, and Enable-Mailbox cmdlet to connect a disabled archive mailbox to an existing mailbox.
Working with soft-deleted mailboxes:
A soft-deleted mailbox will be created when a mailbox is moved from one Exchange mailbox database to another. Exchange will not delete the mailbox completely from the source database after a move, in case if any error occurs during the move that causes the mailbox on the destination database to fail and administrator can always restore the source mailbox and try again.
Administrator can perform either of the below operations on a soft-deleted mailbox:
- Restore it to an existing mailbox.
- Permanently delete it from the Exchange mailbox database.
Ratish Nair
Microsoft MVP | Exchange Server
Team @MSExchangeGuru


