Administrator audit logging in Exchange 2016
Administrator audit logging feature was introduced in Exchange 2010 and it helps to trace the changes made on the exchange server by any user/administrator.
Administrator audit logs contain a record of all the cmdlets and parameters that have been run in both Exchange Management Shell (EMS) and Exchange Admin Center (EAC) are logged under Admin audit logging.
They’re created on-demand when we run the admin audit log report in the EAC, or when we run the New-AdminAuditLogSearch cmdlet in the PowerShell.
NOTE: By default, administrator audit logging is enabled in new installations of Exchange 2016.
Few Important points on Audit logging:
- Cmdlets that are run directly in the Exchange Management Shell are audited.
- Operations performed using the Exchange admin center (EAC) is logged as these operations run cmdlets in the background.
- Cmdlets, regardless of where they’re run, are audited if a cmdlet is on the cmdlet auditing list and one or more parameters on that cmdlet are on the parameter auditing list.
- Get- and Search- cmdlets aren’t logged as Audit logging is projected to show what actions have been taken to modify objects in an Exchange organization rather than what objects have been viewed.
- A cmdlet will not log if an error occurs before the cmdlet calls the Admin Audit Log cmdlet extension agent. If an error occurs after the Admin Audit Log agent is called, the cmdlet is logged along with the associated error.
- Changes to the audit log configuration will be refreshed in every 60 minutes on computers that have the Shell open at the time when the configuration change is made. If changes need to be applied immediately, close and re-open the Shell.
- A command may take up to 15 minutes after its run to appear in audit log search results as the audit log entries must be indexed before they can be searched.
- The admin audit log are stored in a hidden, dedicated arbitration mailbox that can only be accessed by using the EAC, the Search-AdminAuditLog cmdlet, or the New-AdminAuditLogSearch cmdlet
- Administrator audit logging depends on Active Directory replication to replicate the configuration settings that are specify to the domain controllers in the organization. Depending on Active Directory replication settings, the changes will apply to all servers running Exchange in the organization.
- The Admin Audit Log built-in cmdlet extension agent performs admin audit logging of cmdlet operations in Exchange 2016. This agent reads the audit log configuration and then performs an evaluation of each cmdlet run in the organization. If the criteria specified in the admin audit log configuration matches the cmdlet that’s being run, the agent generates an audit log entry.
NOTE: The Admin Audit Log agent is enabled by default, which is required for admin audit logging to function. It can’t be disabled, and its priority can’t be changed.
Admin audit logging configuration:
- By default, a log entry is created every time when a cmdlet runs, other than a Get- or Search-. If required, we can configure audit logging to audit only the cmdlets and parameters which are required by using Set-AdminAuditLogConfig cmdlet.
- When we run the command, Exchange reviews the cmdlet that is used. If the cmdlet that was run matches any of the cmdlets provided with the AdminAuditLogCmdletsparameter, Exchange then checks the parameters specified in the AdminAuditLogParameters parameter. If at least one or more parameters from the parameters list are matched, Exchange logs the cmdlet that was run.
- Changes to the administrator audit log configuration are always logged, regardless of whether the Set-AdminAuditLogConfig cmdlet is included in the list of cmdlets being audited or not and audit logging is enabled or disabled.
Default Admin Audit Logging configuration:

Cmdlets: While configuring the audit logging, we can specify to audit every cmdlet, or only specify the cmdlets needs to be audited using AdminAuditLogCmdlets parameter. To audit all cmdlets, specify only the wildcard character (*). This is the default setting.
Parameters: Can use the AdminAuditLogParameters parameter to specify which parameters must be logged, like with cmdlets, we can specify full parameter names, such as Database, or partial parameter names enclosed in wildcard characters (*), such as *Address*, or a combination of both. To audit all parameters, specify only the wildcard character (*). This is the default setting.
Admin audit log age limit: By default, admin audit logging is configured to store for 90 days. After 90 days, the audit log entry is deleted. You can change the audit log age limit using the AdminAuditLogAgeLimit parameter. Use dd.hh:mm:ss format to specify the value:
Verbose logging: By default, the admin audit log records only the cmdlet name, cmdlet parameters (and values specified), the object that was modified, who ran the cmdlet, when the cmdlet was run, and on what server the cmdlet was run but the admin audit log doesn’t log what properties were modified on the object. If we want the admin audit log to include the properties of the object that were modified, enable verbose logging by setting the LogLevel parameter to Verbose. When the verbose logging is enabled, in addition to the information logged by default, the properties modified on an object, including their old and new values, are also logged in the admin audit log.
Test cmdlets : Cmdlets that begin with Test will not be logged by default. If required we can use TestCmdletLoggingEnabled parameter to$true to enable. It is not recommended to enable logging of test cmdlets always/longer time as test cmdlets can produce a huge number of audit log entries.
Audit Reports under Exchange Administrator console:
The Auditing under Exchange Administrator console has several reports that provide information about various types of compliance and administrative configuration changes. Administrator role group report and Admin audit log report will provide the information about configuration changes in the organization:
- Administrator role group report: Administrator role group report the logs for changes to management role groups that was specified within a specified timeframe. The results includes the role groups that have been changed, who changed them and when, and what changes were made. A maximum of 3,000 entries can be returned. If your search might return more than 3,000 entries, use the Administrator audit log report or the Search-AdminAuditLog cmdlet.
- Admin audit log report: Admin audit log report provides the admin audit log recorded within a specified timeframe. We can also export admin audit log entries to a XML file and then send the file via email to a recipient you specify.
Let us see how search and export the Admin Audit log report in Exchange 2016:
Open EAC and Navigate to Compliance Management à Click on Auditing:

Run the Admin Audit Log Report:
Open EAC and Navigate to Compliance Management à Select Auditingà Click on Run the Admin Audit Reportàunder view Administrator Audit log window specify the time frame and click on Search and we can see the result as below:

Export Admin Audit Log Report:
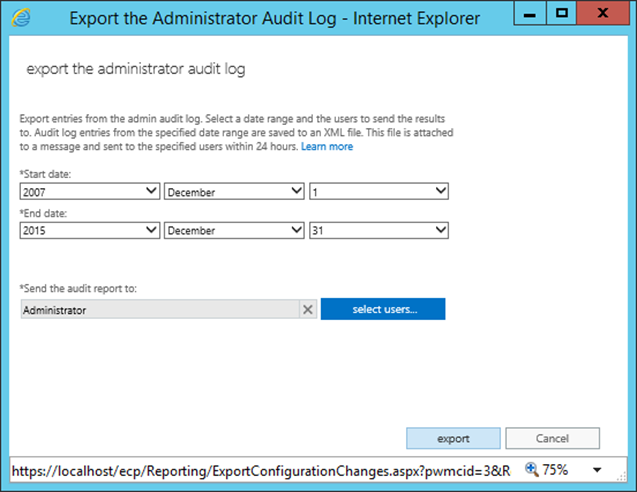
Open EAC and Navigate to Compliance Management à Select Auditingà Click on Export the Admin Audit Reportàunder Export the Administrator Audit log window specify the time frame and the user to whom the report needs to sendàclick on Export:
PowerShell commands:
Below are the few commands which will be users with Admin Audit loggings:
New-AdminAuditLogSearch, Search-AdminAuditLog, Write-AdminAuditLog, Set-AdminAuditLogConfig
are the common cmdlets normally use in Admin Audit loggings
Example:
Set-AdminAuditLogConfig -LogLevel Verbose
Search-AdminAuditLog –Cmdlets New-SendConnector –StartDate mm/dd/yyy – EndDate mm/dd/yyy
New-AdminAuditLogSearch –Name “Hold-case001” –Cmdlets Set-Mailbox – StartDate mm/dd/yyy – EndDate mm/dd/yyy –StatusMailRecipients <Recipient email address>
Ratish Nair
Microsoft MVP | Exchange Server
Team @MSExchangeGuru



January 3rd, 2016 at 5:11 pm
[…] Administrator audit logging in Exchange 2016 […]
January 3rd, 2016 at 5:13 pm
[…] Administrator audit logging in Exchange 2016 […]
January 3rd, 2016 at 5:20 pm
[…] Administrator audit logging in Exchange 2016 […]
July 10th, 2016 at 8:18 pm
[…] Administrator audit logging in Exchange 2016 […]