Exchange 2016: New Features in compare to Exchange 2010
Most of us who would be looking to migrate to Exchange 2016 are currently using Exchange 2010. So it is important to know the changes coming in Exchange 2016. This is so important for Exchange 2010 users because Exchange 2016 has many architectural changes. Many features have been added and removed as well.
This is the first step of Exchange 2010 to 2016 migration.
More than migration you would like to know what are the changes you will face from user point of you. This will help preparing you to communicate and prepared for new changes and avoid any outages.
Previously we have discussed Exchange 2016 changes in compare to Exchange 2013 here. Some of the features will repeat in this blog. Let us check new features.
New Features in compare to Exchange 2010
Exchange Management Console:
EMC will show very limited tool unlike Exchange 2010. Microsoft had observed the delayed update in EMC and decided to for better Admin console which will be used in Exchange 2016 to manage from GUI.
Exchange Admin Center:
Microsoft gave you the taste of Exchange Admin Center in Exchange 2010 in the name of Exchange Control Panel and in Exchange 2013 we got all configurations to EAC. Same continues in Exchange 2016. You can connect from anywhere to you EAC using a web browser. It is one console for all. Public Folders are mailboxes so no separate console required. Many Gui features have moved to Exchange management shell like Queues. EAC refresh is much quicker than Exchange 2010 Exchange management console. Description can be checked here.
Exchange 2016 Architecture:
Exchange 2016 reduced to only 2 Roles which can’t be installed together. You might have guessed it Mailbox Role and Edge Transport Role.
Hub Transport, Unified Messaging and Client Access Role has been merged to Mailbox Role. So Time to say bye to Hub Transport, Unified Messaging and Client Access Roles.
Mailbox Server Role will allow HTTP, POP, IMAP and SMTP client access protocols. This means time to say bye to RPC and RPC CAS Array.
Edge Transport: Edge transport role is coming in the RTM version. So no longer SP1 wait.
Exchange 2016 architecture will provide the following benefits:
- Upgrade flexibility: Unlike Exchange 2010 we have only one role so we don’t have to worry about which server role should be patched first.
- Session Affinity: In Exchange 2010 we used session affinity for many protocols which is not required because we have CAS and mailbox role on the same server.
- Simplicity: Less number of namespace requirements in compare to Exchange 2010. One for protocols and one for autodiscover is required.
- Outlook can connect only using Outlook Anywhere with either MAPI over HTTP or RPC over HTTP.
- Mailbox high availability is still provided by Database Availability Group which has reduced failover time.
- The Exchange Store service has been re-written in managed code.
- Each Database runs under its own process which allows the isolation of store issue to a single database.
Managed Store
In Exchange 2016 Information Store has 2 processes Microsoft.Exchange.Store.Service.exe and Microsoft.Exchange.Store.Worker.exe which is called Managed Store.
The Managed Store is written in C# and integrated with Microsoft Exchange Replication Service. This provides improved resiliency.
Managed store also enables more granular management of resource consumption and faster root cause analysis through improved diagnostics
Managed Store manages mailbox databases through Microsoft Exchange Replication Service and continues to use our old and favorite Extensible Storage Engine (ESE) database engine. Microsoft Exchange Replication Service is responsible for mailbox servers service availability.
Managed Store also enables faster database failover and improved physical disk failure handling.
Managed store is integrated with the search Foundation Search Engine which provides more robust indexing and search.
Certificate Management
In Exchange 2010 we had required to install certificate per server from Exchange Management Console. In Exchange 2016 you can install certificate into multiple servers in one go using Exchange Admin Center. You will also see the certification expiry notification in EAC as well.
Setup
Improved Readiness Checks:
Readiness checks run faster than previous Exchange setups and it is capable of installing required windows features.
Simplified and modern wizard:
Only required steps left in the setup wizard.
Office 365 Hybrid
HCW: The Hybrid Configuration Wizard which was included in Exchange 2013 is has become a cloud-based application. In Exchange 2016, you will download then install the Hybrid Configuration Wizard. The wizard will function same as Exchange 2013 but expect few new benefits:
- The Hybrid Configuration wizard can be updated quickly to support changes in the Office 365 service.
- The wizard can be updated to account for issues detected when you try to configure a hybrid deployment.
- Improved diagnostics and troubleshooting to resolve issues which came while running the wizard.
-
The same wizard will be used by everyone configuring a hybrid deployment if you are using Exchange 2013 or Exchange 2016.
AADConnect Improvement: Multi-forest hybrid deployments has become simple when we use Azure Active Directory Connect (AADConnect). AADConnect introduces management agents that will make it significantly easier to synchronize multiple on-premises Active Directory forests with a single Office 365 tenant.
New Authentication:
Hybrid deployments will now support the new modern authentication model in Outlook which we discussed earlier.
ActiveSync:
Exchange ActiveSync clients will be seamlessly redirected to Office 365 when a user’s mailbox is moved from on premise to Exchange Online. Exchange ActiveSync clients should support HTTP 451 redirect. We already discussed about this attribute change here.
Outlook on the Web (old name OWA):
Outlook web app is new Outlook on the Web
It will support Microsoft Edge, Internet Explorer 11 and most recent version of Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome and Safari Browsers.
The following new features will be added:
- Platform-specific experiences for phones for Android and IOS.
- Premium Android experience for chrome on Android version 4.2 or later devices.
- Email improvements: A new single-line view of the Inbox with an optimized reading pane, emojis, archiving and the ability to undo mailbox actions like moving a message or deleting a message.
- Contact linking: Users can to add contacts from their LinkedIn accounts.
- Calendar: New look and new features, including email reminders for Calendar events, ability to propose a new time in meeting invitations, birthday calendars and improved search.
- Search suggestions and refiners for an improved faster search. Search suggestions. Search refiners will help a user more easily find the information they’re looking for by providing contextually-aware filters. Filters might include date ranges, related senders, and so on.
- New themes: 13 new themes with graphic designs.
- Options for individual mailboxes have been renewed.
- Pins and Flags: This allow users to keep essential emails at the top of their inbox (Pins) and mark others for follow-up (Flags). Pins are folder specific, great to use folders to organize emails. Quickly find and manage flagged items with inbox filters or the new Task module.
- Performance improvements in a number of areas across Outlook on the web, including creating calendar events, composing, loading messages in the reading pane, search, startup, pop outs and switching folders.
- Apps for Outlook: Outlook Apps allow users & administrators to extend the capabilities of Outlook on the web
- Link preview: This enables users to paste a link into messages and Outlook on the web automatically generates a rich preview to give recipients a peek into the contents of the destination. This also works with video links. So every link will generate the preview and you have option to remove the preview. Preview is always good because it gives the intro of the link.
-
Offline Mode: In Exchange 2016 you can use OWA renamed to OOTW in offline mode without internet. This means you don’t need to but outlook license and you can continue to read and write emails without internet in OOTW. I am sure this feature makes you happy.
Let us see how it works. Internet Explorer 11 & Windows Store apps using JavaScript support the AppCache as defined in the HTML5 specification. This allows you to create offline web applications. AppCache enables webpages to cache resources locally, including images, script libraries, style sheets, & so on. In addition, AppCache allows URLs to be served from cached content using standard Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) notation. Amazing so far.
The following web browsers support AppCache and you can use them for OOTW offline mode. Remember this is a key to reduce office licenses.
- Microsoft Edge
- Internet Explorer 11 or later versions
- Google Chrome 44 or later versions
- Firefox 39 or later versions
- Safari 8 or later (only on OS X/iOS) versions
- Microsoft Edge
Support for Modern Authentication for Outlook:
Exchange 2016 supports Active Directory Authentication Library authentication model in outlook clients on Windows and other OS. ADAL will enable 2 factor authentication which helps in securing the data for many security organizations. More details are here.
MAPI over HTTP
MAPI over HTTP is the default protocol in Exchange 2016 which outlook uses to connect and communicate with Exchange server. It is more reliable and stable protocol at the Transport layer of the OSI model which can find higher level transport errors and enhance recovery. One of the best feature of this protocol is that it can pause and resume the outlook connection which allows outlook to change networks and resume from hibernation. If outlook client does not support this protocol, then they will continue to connect using Outlook Anywhere.
If you are installing Exchange 2016 in the mixed mode, then you will see a warning as shown below while running Exchange 2016 setup.
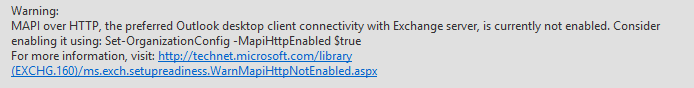
You need to run the following command to enable it.
Set-OrganizationConfig –MapihttpEnable $true

Now your outlook will show like this.
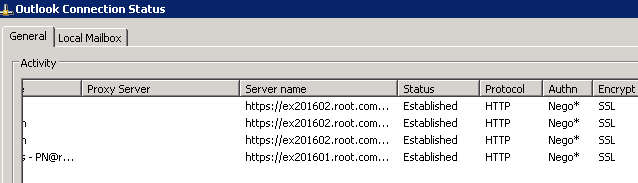
Document Collaboration
Outlook on the web will enable users to link to and share documents stored in OneDrive for Business or in an on-premises SharePoint server in place of attaching a file to the message. It will be similar to current Office 365 users.
If a Word, Excel, or PowerPoint file stored in on-premises SharePoint or OneDrive for Business is included in an email received by a user on Exchange 2016, the user will now have the option of viewing and editing that file in Outlook on the web alongside the message (“Office Web Apps vNext” server must be deployed in your on-premises organization to get this feature). If you are editing attachment, then user should have an Office client license.
Few more improvements are coming which are mentioned below:
- Save a file to OneDrive
- Upload a file to OneDrive
- Most Recently used lists populated with both local and online files.
Mail flow:
Exchange 2016 changed the Transport architecture completely. The brief overview of the changes is mention below:
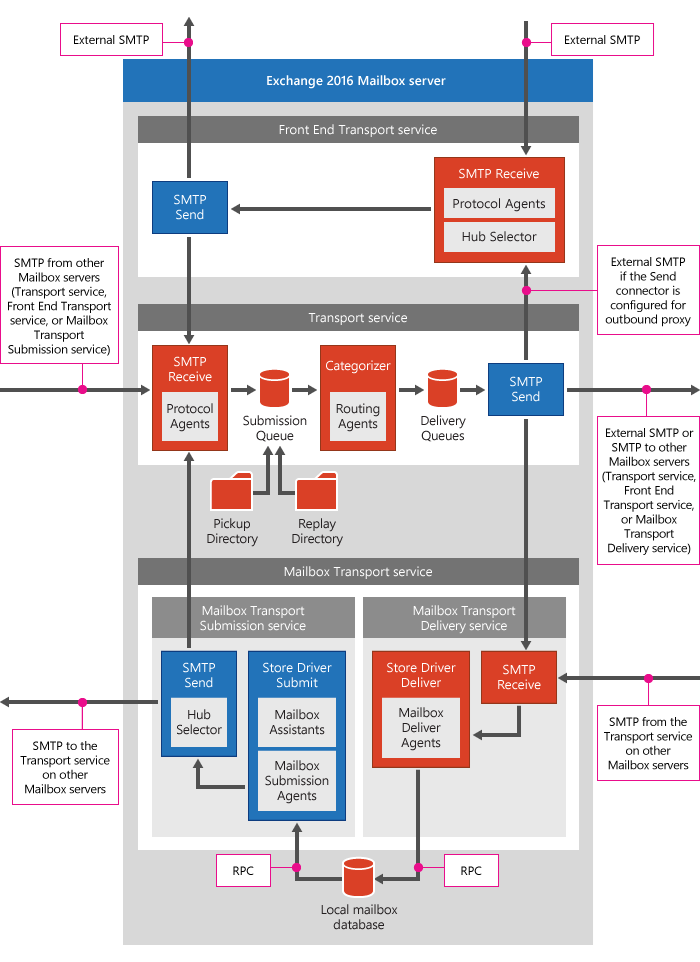
Transport pipeline:In Exchange 2016 the transport pipeline has several different services: The Front End Transport service, the Transport service, and the Mailbox Transport service. This is same as Exchange 2013 so I would recommend watching my session on Transport here.
Routing:Mail routing in Exchange 2016 recognizes DAG boundaries as well as Active Directory site boundaries. Also, mail routing has been improved to queue messages more directly for internal recipients.
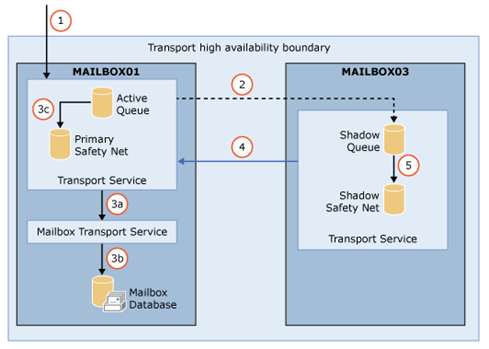
SafetyNet: Exchange 2016 transport dumpster has been improved and renamed to Safety Net.
Safety Net introduces the concept of the Primary Safety Net and the Shadow Safety Net. If the Primary Safety Net is unavailable for more than 12 hours, resubmit requests become shadow resubmit requests, and messages are re-delivered from the Shadow Safety Net.
Safety Net takes over some responsibility from shadow redundancy in DAG environments. Shadow Redundancy duplicates email to the Mailbox Server in the 2nd AD site and delay acknowledgement.
Shadow redundancy doesn’t need to keep another copy of the delivered message in a shadow queue while it waits for the delivered message to replicate to the passive copies of mailbox database on the other Mailbox servers in the DAG. The copy of the delivered message is already stored in Safety Net, so the message can be resubmitted from Safety Net if necessary. Check details description here.
Check the safety net flow.
-
Connectors The default maximum message size for a Send connector or a Receive connector, as specified by theMaxMessageSize parameter, has been increased from 10MB to 25MB. Same as Exchange 2010 we have send and receive connectors.
You can set a Send connector in the Transport service of a Mailbox server to route outbound mail through a Front End transport server in the local Active Directory site, by means of the FrontEndProxyEnabled parameter of the Set-SendConnector cmdlet, thus consolidating how email is routed from the Transport service.
Receive connector: We can configure FrontEnd Transport or Hub Transport role. FrontEnd connects over port 25 and Hub Transport connects over port 2525. You would like to bypass FrontEnd so you need to ensure you sending traffic on port 2525 from spam guard.
You can continue to use Exchange Edge Transport server. Exchange 2016 comes with Edge Transport server.
Have a look on Transport architecture picture from Technet
Data Loss Prevention
As well all know DLP has been part of Exchange 2013 success story which is a business standard requirement for many financial org now. DLP has improved and added more templates for other countries now. Improved DLP in Exchange 2016 we can now identify, monitor, and protect 80 different types of sensitive information. Sensitive information types inventory can be checked here.
Transport Rules
I am sure you are familiar with transport rule which works and server level and configurable for the whole ORG.
Exchange 2016 is adding following new features to the transport Rules:
-
Exchange transport rules can now identify 80 different types of DLP configuration which we discussed earlier.
-
There is a new condition “Any attachment has these properties, including any of these words”,has been added which checks the attachment property for the specific words. This new condition easily integrates your Exchange transport rules and DLP policies with SharePoint Server, Windows Server 2012 R2 File Classification Infrastructure (FCI), or a third-party classification system.
-
There is a new action added Notify the recipient with a message. A transport rule can be set to send a notification to the recipient with the text you specify which can inform the recipient that the message had some issues and actions required.
-
There is another new action Generate incident report and send it to has been updated so that multiple distribution lists can receive the incident report
-
There are additions in predicates and actions.
In-place Archiving, retention and eDiscovery
Exchange 2016 has added the following improvements for In-Place Archiving, retention, and eDiscovery:
-
Public folder support for In-Place eDiscovery and In-Place Hold
Exchange 2016 has integrated public folders into the In-Place eDiscovery and Hold workflow. In Exchange 2016 in-Place eDiscovery can search public folders and we can put In-Place Hold on public folders. We can also configure a query-based and a time-based hold on public folders. We can only search and place a hold on all public folders right now but later Cumulative Updates will allow you to choose specific public folders to search and place on hold.
-
Compliance Search
Exchange 2016 is introducing a new eDiscovery search tool called Compliance Search. This tool is capable of running a single search for very large numbers of mailboxes. There is no limit on the number of mailboxes, so all mailboxes can be searched in one search. There is no limit on the number of searches that can run at the same time.
We can run compliance Search from Exchange Management Shell. Compliance Search commands can be found here.
An administrator or eDiscovery manager must be assigned the Mailbox Search management role or be a member of the Discovery Management role group to run the compliance search commands.
-
In-Place Hold In-Place Hold is a unified hold model which allows you to meet legal hold requirements in the below mentioned scenarios:
-Preserve the results of the query which is also called query-based hold. This allows for scoped immutability across mailboxes.
-Place a time-based hold to meet retention requirements.
-Place a mailbox on indefinite hold. This is the one similar to litigation hold in Exchange 2010. You might have used it.
-Place a user on multiple holds.
-
In-Place eDiscovery In-Place eDiscovery allows authorized users to search mailbox data across all mailboxes and copy messages to a discovery mailbox for review which is similar to Exchange to Exchange 2010 but in Exchange 2016 you can run one query for all mailbox, in Exchange 2010 you need to run one query per mailbox. Exchange 2016 In-Place eDiscovery allows discovery managers to run more efficient searches and hold.
-Federated search – This Search allows us to search and preserve data across multiple data repositories. In Exchange 2016, you can perform in-place eDiscovery searches across Exchange, SharePoint 2013, and Skype for Business. You can use the eDiscovery Center in SharePoint 2013 to perform In-Place eDiscovery search and hold. Off course this search requires federation configuration with SharePoint 2013, and Skype for Business.
-Query-based In-Place Hold – This search allows us to save the results of the query which allows for scoped immutability across mailboxes.
-Export search results Discovery Managers can export mailbox content into a .pst file from the SharePoint 2013 eDiscovery Console. At the same time Mailbox export request cmdlets are no longer required to export a mailbox to a .pst file. I am sure you will miss this feature. We will try to request to get this feature back.
-Keyword statistics Search statistics are offered on a per search term basis. This enables a Discovery Manager to quickly make intelligent decisions about how to further refine the search query.
-KQL syntax Keyword Query Language (KQL) is new. Discovery Managers can also use Keyword Query Language (KQL) syntax in search queries. KQL is similar to Exchange 2010 discovery search’s Advanced Query Syntax (AQS).
-In-Place eDiscovery and Hold wizard Discovery Managers can use the In-Place eDiscovery & Hold wizard to perform both eDiscovery and hold operations.
If there is no SharePoint, then you will have a subset of eDiscovery in the Exchange Admin Center.
-
Search across primary and archive mailboxes in Outlook on the web You don’t need to run 2 separate searches, “Outlook on the web” can search primary and archive mailboxes in one query.
-
Archive Skype for Business content Now in Exchange 2016, you can archive Skype for Business content from a mailbox. You can also place Skype for Business content on hold using In-Place Hold & use In-Place eDiscovery to search Skype for Business content archived in Exchange.
Microsoft Rights Management connector:
In Exchange 2016 we get an optional application called Microsoft Rights Management connector (RMS connector) which helps you enhance data protection by connecting to cloud-based Microsoft Rights Management services.
Once you deploy and configure the RMS connector, it provides continuous data protection throughout the life span of the information. You can always define the level of protection you need. Isn’t it incredible????
Auditing:
-
Auditing reports: In Exchange 2016 EAC includes auditing functionality which allows us to run reports or export entries from the mailbox audit log and the administrator audit log. The mailbox audit log records whenever a mailbox is accessed by someone other than owner of the mailbox. This helps determining who has accessed a mailbox & what they have done. The administrator audit log records any action, based on an Exchange Management Shell cmdlet, performed by an administrator. This helps during investigation and troubleshooting configuration issues and the cause of problems which may be related to security or compliance.
-
Viewing the administrator audit log We can view administrator audit log entries in the EAC, in place of exporting the administrator audit log because it can take up to 24 hours. We can view it if you go to Compliance Management > Auditing and click View the administrator audit log. This will display upto 1000 entries on multiple pages.
Anti-malware protection:
The Exchange 2016 has very strong built-in malware filtering capabilities which helps in protecting your network from malicious software transferred through emails. All emails sent or received by Exchange 2016 are scanned for malware (viruses and spyware). If malware is detected, the message is deleted. Notifications can be sent to senders or administrators when an infected message is deleted and not delivered. We can choose to replace infected attachments with either default or custom messages that notify the recipients of the malware detection.
Recipients:
Exchange 2016 Recipients managements are following:
-
Group Naming Policy: Now we can create group naming policy which will allow us to set Distribution Group names as per company policy. This allow us blocking some words. We can specify a prefix and suffix for the group. In EAC, select Groups then more … then click on Configure group naming policy.
You can run the following command to check the policy
Get-OrganizationConfig | FL DistributionGroupNamingPolicy
Sharing and collaboration:
Let us see the sharing and collaboration enhancements in Exchange 2016.
-
Public folders: Public Folders are Public Folder mailboxes in Exchange 2016 which reside in the mailbox database. So they can take advantage of the existing high availability and storage technologies of the mailbox store. The public folder architecture uses specially designed mailboxes to store both the hierarchy and the public folder content. There is no PF Database and No PF replication. Now Exchange 2016 uses single-master replication model.
Check out my Public Folders Then Public Folders Migration blog. There is a PF migration video on YouTube channel as well.
-
Shared mailboxes: Shared mailbox creation and administration has improved in Exchange 2016. Now we can create a shared mailbox in one step from Exchange admin center. In EAC, go to Recipients
à Shared Mailboxes to create a shared mailbox. -
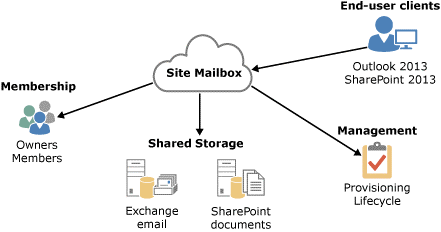
Site Mailboxes: In Exchange 2016 we can use site mailbox to keep the document and emails where emails stay in the mailbox database and documents goes to the SharePoint. Site mailboxes improve collaboration and user productivity by allowing access to both Microsoft SharePoint 2013 documents and Exchange email using the same client interface. A site mailbox is functionally comprised of SharePoint 2013 site membership (owners and members), shared storage through an Exchange 2013 mailbox for email messages and a SharePoint 2013 site for documents, and a management interface that addresses provisioning and lifecycle needs. Check out the below mentioned document.
Integration with SharePoint and Skype for Business
Exchange 2016 offers great integration with Skype for Business and SharePoint 2016. There are following benefits of this enhanced integration:
- Exchange 2016 can archive Skype for Business Server 2015 content & it uses Exchange 2016 as a contact store.
- Discovery Managers can run Hold searches & In-Place eDiscovery across Exchange 2016, SharePoint 2013 and Skype for Business data.
Batch Mailbox Moves:
In Exchange 2013 Microsoft started batch mailbox and public folders migration moves which will continue in Exchange 2016. This is built over Mailbox Replication service moves with enhanced management capability. You can give a path of csv file to pull the input as well.
The following enhancements comes in the batch moves.
- Ability to move multiple mailboxes in large batches.
- Email reporting notification.
- Automatic moves retry and automatic prioritization.
- Primary and personal archive mailboxes can be moved together or separately.
- Option for manual move request finalization. This allows us to review a move before we complete it.
- Periodic incremental syncs to migrate the changes.
High Availability and Site Resilience:
Exchange 2016 also uses DAGs and mailbox database copies for high availability with single item recovery, retention policies, lagged database copies and Exchange native data protection. The high availability platform, Information Store and the Extensible Storage Engine (ESE), have been enhanced to provide greater availability, easier management & to reduce costs.
At the same time there are many enhancements included in Exchange 2016 which are mentioned below:
- Managed availability: This is one of the best new feature which provides internal monitoring & recovery-oriented features are tightly integrated to help prevent failures, proactively restore services, and initiate server failovers automatically or alert administrators to take action. Wohoo. Isn’t it awesome. Go home and sleep now. The will also provide better end user experience rather than just server and component uptime to help keep the service continuously available.
- Managed Store: We already discussed this new enhancement provide higher availability through improved resiliency.
- Support for multiple databases per disk Exchange 2013 supports multiple databases (1 active and other passive copies) on the same disk. This allows leveraging larger disks in terms of capacity and IOPS as efficiently as possible.
- Automatic reseed: AutoReseed is a magic of reseeding which automatically reseed if same size spare disk is available. Have a look on my blog here. So if a disk fails in the mid night, you don’t need to wake up, continue sleeping and Exchange 2016 will automatically reseed your database copy. Auto Reseed first introduced in Exchange 2013 and continued to Exchange 2016.
- Automatic recovery from storage failures: This feature continues Exchange 2010 innovation to allow the system to recover from failures that affect resiliency or redundancy. In addition to Exchange 2010 bugcheck behaviors, Exchange 2016 also includes recovery behaviors for long I/O times, excessive memory consumption by MSExchangeRepl.exe, & severe cases where the system is in such a bad state that threads can’t be scheduled. Super awesome feature.
- Lagged copy enhancements In Exchange 2016 lagged copies can take care of itself to a certain extent using automatic log play down. Now lagged copies will play down log files in many situations like single page restore or low disk space. If Exchange Server detects that page patching is required for a lagged copy, the log files will be automatically replayed into the lagged copy to perform page patching. Lagged copies will invoke this auto replay feature when a low disk space threshold has been reached & when the lagged copy has been detected as the only available copy for a specific period of time. Lagged copies can also leverage Safety Net (discussed earlier) which makes recovery or activation much easier.
- Single copy alert enhancements: The single copy alert introduced in Exchange 2010 is no longer a separate scheduled script. Now it’s integrated into managed availability components within the system & is a native function within Exchange.
- DAG network auto-configuration: In Exchange 2016 Database Availability Group networks can be automatically configured by the system based on configuration settings. DAGs can distinguish between MAPI & Replication networks then configure DAG networks automatically.
- No need of Cluster administrative access point: Since Exchange 2013 SP1 we have an option to create DAG with no IP and cluster administrative access point. This has already taken care multiple issue around IP DAG. In Exchange 2016 Default DAG creation will be without IP and cluster administrative access point so it is recommended to install Exchange 2016 on Windows 2012 R2 or higher. Check out my blog on it here.
Exchange Workload Management:
The Exchange workload is Exchange server feature, protocol, or service that has been explicitly defined for the purpose of Exchange system resource management. Each Exchange workload consumes system resources like CPU, mailbox database operations, or Active Directory requests to execute user requests or run background work. The examples of Exchange workloads are Outlook on the web, Exchange ActiveSync, mailbox migration, and mailbox assistants.
Exchange 2016 has following two ways to manage Exchange workloads:
- Monitor the health of system resources: Managing workloads based on the system resources health.
- Control how resources are consumed by individual users: Controlling how resources are consumed by individual users was possible in Exchange 2010 which was called user throttling and this capability has been enhanced in Exchange 2016.
Discontinued Features from Exchange 2010 to 2016:
Architecture:
Hub Transport Server Role:
Time to say bye to the Hub transport role. This role has been merged as transport services in Exchange 2016 mailbox role.
Client Access Server Role: This role has been merged as client access services in Exchange 2016 mailbox role
Time to say bye to Client Access server role. In Exchange 2016 Microsoft has removed Client Access server role and added Client Access server Services. Mailbox role is the only role left and it performs all the action.
This is good move but Exchange will no longer be able to leverage windows network load balancing and DAG in the same infrastructure which was the option for small org rather than investing in Load Balancers.
On the other hand, Load Balancer are designed to do load balancing which adds much more efficiency to the load balancing so we should load balancers. There are virtual load balancers available which can be installed just like Client Access server role in Virtualization.
Unified Messaging Server Role:
Time to say bye to the unified messaging role. This role has been merged as unified messaging services in Exchange 2016 mailbox role
MAPI/CDO Library:
Time to say bye to the MAPI/CDO library. In Exchange 2016 Exchange Web Services (EWS), Exchange ActiveSync (EAS), and Representational State Transfer (REST) APIs has replaced MAPI/CDO library. If an application in your organization is using the MAPI/CDO library, in Exchange 2016 it needs to move to EWS, EAS, or the REST APIs.
EMC and ECP:
EMC and ECP are going away and all controls are coming into Exchange Admin Center. EAC uses same ECP virtual directory so don’t be surprised.
Client Access:
Outlook RPC/MAPI:
Time to say bye to RPC/MAPI. Outlook anywhere is the only method to connect your outlook to Exchange 2016. MAPI over http is the default protocol and alternative is RPC over http. Outlook 2013 SP1 or higher support MAPI over http.
Outlook 2003 and 2007:
Outlook 2003 and 2007 are not supported in Exchange 2016. Outlook 2003 was not supported in Exchange 2013 and in Exchange 2016 outlook 2007 will also say bye to us.
OWA(OOTW) and Outlook:
Spell Check: Bye to built-in Spell checker. Now OOTW will use web browser’s spell checker.
Customizable filters:
OOTW no longer has customizable filtered views & no longer supports saving filtered views to Favorites. Customizable filters have been replaced by fixed filters that can be used to view all messages, unread messages, messages sent to the user, or flagged messages. This is awesome.
Message flags: Custom dates can only set from outlook. OOTW does not support it.
Chat Contact list: Time to say bye to the chat contact list that appeared in the folder list in Exchange 2010 OWA
Search folders: OOTW does not support searching folders. It might be added later.
Mailflow:
Linked Connectors:
In Exchange 2016 you can’t link a Send connector to a Receive connector. LinkedReceiveConnector parameter has been removed from New-SendConnector and Set-SendConnector.
Anti-spam and Anti-malware:
Anti-spam agent management in the EMC:
No more GUI management of Anti-spam and anti-malware. We can only configure it from Exchange management shell.
Connection Filtering agent on Hub Transport servers:
In Exchange 2016 the Attachment Filter agent and the Connection Filtering agent aren’t available.
The only way to install Connection Filtering agent is to configure it on Edge transport server or find a tweak which I explained in my transport session to install on mailbox role.
Managed policy and Compliance:
Managed Folders:
In Exchange 2010, we all have used managed folders for messaging retention management. In Exchange 2016 managed folders are saying Bye to us which has replaced by Retention Policies and TAGs for MRM.
Port Managed Folder Wizard:
In Exchange 2010, we have used the Port Managed Folder wizard to create retention tags based on managed folder & managed content settings. This to say bye to this functionality. In Exchange 2016, the Exchange admin center doesn’t include this functionality. We have to use the command New-RetentionPolicyTag with the parameter ManagedFolderToUpgrade to create a retention tag based on a managed folder. This can be used to migrate the managed folders to retention tag.
Unified Messaging and Voice Mail:
Directory lookups using Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR):
In Exchange 2010, Outlook Voice Access users have used speech inputs using Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) to search for users listed in the directory. Speech inputs have also been used in Outlook Voice Access to navigate menus, messages, and other options. However, we still required to use the telephone key pad to enter their PIN, and navigate personal options.
Now in Exchange 2016, authenticated & non-authenticated Outlook Voice Access users cannot search for users in the directory using speech inputs or ASR in any language. So this feature has gone for good.
Now callers who call into an auto attendant can use speech inputs in multiple languages to navigate auto attendant menus and search for users in the directory.
Reference: https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj150540(v=exchg.160).aspx
It’s the beginning. More to come.
Microsoft MVP | Exchange Server
Team@MSExchangeGuru



October 1st, 2015 at 3:09 am
[…] Next UP: New Features in compare to Exchange 2010 – Check out here. […]
November 26th, 2015 at 12:38 pm
Very good information to explain Exchange 2016
August 18th, 2016 at 3:41 pm
Not sure why, but the EMC blows away the EAC. EMC might be slower but atleast you get things done on it. The EAC is missing alot. Why didn’t Microsoft provide both options?
August 18th, 2016 at 7:09 pm
EMC used to show wrong info,EAC is much better. Most of the daily task are available and for rest learn EMS because Powershell is very useful, you can do much more in less time in Powershell
August 29th, 2016 at 3:40 pm
My main problem with the shell is, once a month I might need to preview a dynamic distribution group to see if the person shows up. Since I don’t do that enough I always have to search the internet for the right command to use. If there is a quicker way then maybe the shell wouldn’t be bad.
August 31st, 2016 at 4:05 am
Save the command in a notepad and save as .ps1
you can just run this PS1 file in your EMS whenever you need.
March 11th, 2017 at 8:56 pm
Is Single Instance Storage coming back in E2016?
March 11th, 2017 at 9:13 pm
No.
September 19th, 2017 at 11:20 am
What is the alternate of “LinkedReceiveConnector” in E2016?